Challenges for soilless farming and industry preparedness to address these challenges
Soilless farming is an innovative technology that forgoes the soil associated challenges such as poor soil quality, soil pests, soil arability, etc that hamper the growth of the plants. Although soilless farming has quite a few advantages over traditional farming, its adoption as an alternative farming technique has not been smooth, which might be attributed to:
- High Initial Capital Costs: Initial investments for setting up the infrastructure for soilless farming is very high and depends on the complexity of technological inputs for various types of set-up. The maintenance costs is also high owing to the use of electricity, lights and maintenance of a controlled environment.
- Expert Knowledge: Soilless farming requires skilled labour to maintain appropriate growing conditions to cultivate the plants. Plants react very quickly to poor/good nutrition, so the person must have the requisite expert level knowledge for maintaining the controlled environment and troubleshooting, if required. It is critical that the expert has the knowledge of the technical know-how for successful operations of soilless farming.
- Optimization for each crop: For soilless farming, optimization needs to be done for every crop as it is uncertain, how each crop will react to the absence of soil. Also, the nutrient uptake and environmental conditions for achieving higher yields must be optimized for each crop. Soil microbes play an important role in nutrient uptake and the final composition of nutrients in the plants. The crop physiology and agronomy needs to be thoroughly studied and replicated. As the crops are grown in closed systems, manual pollination is relied on which is expensive and tedious.
- Water and nutrient requirements: Nutrient costs are high and nutrient solutions must be optimized for every crop. The water required for soilless farming should be of a specific quality, otherwise the yields will be affected. The costs for maintaining good quality of water also adds to the operational costs.
- Disease Management: Although soilless farming restricts the soil borne diseases, any other disease due to non-maintenance of proper growing environment will spread rapidly within a confined condition due to shared water and nutrients. This will lead to poor yields and affect the economic returns adversely.
In places with mild climate variation, and where low-tech greenhouses are currently in use, the use of soilless farming is not justified as the costs of soilless systems are not always recovered by higher yields; other factor such as high equipment costs and low return on investments may limit production. Unless there are critical problems with soil, water shortage or the environmental pollution by nutrient leaching is serious (Savvas and Gruda, 2018), the wide commercial adoption of this technology will be limited.
To address these challenges, the industry is optimizing solutions such as use of LED lights to reduce electricity consumption and lesser heat emission to reduce the carbon footprint. Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine learning (ML) are being explored for optimizing conditions for soilless farming to reduce the reliability on skilled labour. Extensive research is being done on managing diseases, nutrient uptake and maintaining quality of water.
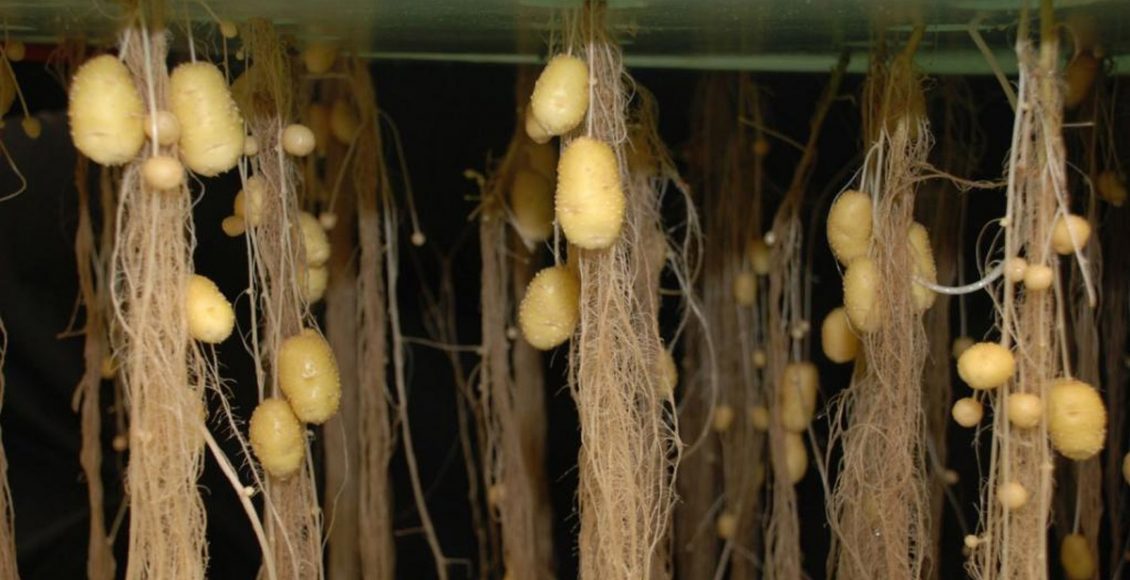
Indian industry players have been actively adopting global technologies and working on solutions to overcome these challenges. To ensure that the plants do not suffer from stress or strain of less and over watering, Jain irrigation Systems has designed a suitable and affordable grower which protects the plants and delivers a measured quantity of water at the root zone of each plant at regular intervals. ITC also has developed a system where the water used for hydroponics may be reused after peroxide disinfection and nutrient reintegration through conductivity control allow the utilization of water and nutrients that otherwise would be lost. Another example is the production of high quality sweet potato seed production by Central Potato Research Institute using aeroponics. The aeroponic system offers the potential to 3-4 times increase in the number of minitubers per plant.
Industry has been working relentlessly on overcoming the challenges and the Government has also been supporting these efforts by providing subsidies. Overcoming the various challenges will definitely boost the adoption of soilless farming and change the farming outlook across the globe.
Author

Connect with Authors at: E-mail agribusiness@sathguru.com
 Grow Beyond
Grow Beyond