Harvesting Hope: Tackling Post-Harvest Losses in India’s Fruit and Vegetable Industry
Introduction
India is a rich and diverse agricultural nation, known for its vast production of fruits and vegetables. However, the country also faces significant post-harvest losses in this sector, which diminishes both economic opportunities and food security. The primary focus of the agriculture and food sector has always been on increasing yield and productivity, but the resources are limited there should be focus on managing the food loss and waste which is almost around 30%. In this blog post, we will explore the reasons behind these losses and discuss the government interventions and disruptive solutions that aim to address the issue. Additionally, we will examine the current trends in the market and advancements in the processing of fruits and vegetables.
Perishability Issues in the Fruits and Vegetables Market
In the dynamic landscape of the Indian agricultural sector, the management of perishability poses a significant challenge, particularly in the realm of fruits and vegetables (F&V). The intricacies of transportation, storage, and distribution demand innovative solutions to mitigate losses and ensure sustained freshness. One of the main factors contributing to the short shelf life of F&V is their natural ripening process. As fruits and vegetables ripen, they release ethylene gas, which can speed up the ripening process of other nearby produce. This can result in over-ripening and spoilage if not properly managed. Careful monitoring of ethylene levels in storage and display areas is necessary, and stakeholders must take appropriate measures to prevent cross-contamination. Post-harvest losses in India remain excessively high, with a substantial quantity of fruits and vegetables succumbing to inefficient post-harvest processes. This inefficiency contributes to a significant disparity between gross production and net availability. According to a study published by NABARD in 2020, post-harvest handling is responsible for 20-30% of losses across various stages, including storage, grading, packaging, shipping, and marketing, whether as fresh produce or in processed form. These losses occur primarily in the farmer’s field (15-20%), during packaging (15-20%), transportation (30-40%), and marketing (30-40%). The total food loss in India is accounted to INR 1,52,000 Cr.
Challenges in Perishability and Post-harvest Losses:
-
- Inadequate Cold Chain Facilities: The main issue in India is not the lack of cold storages but the lack of pre-cooling and connectivity at farmgate. According to a report from the National Centre for Cold-chain Development, the gap in cold storage infrastructure was only 8% (2020), but in Reefer Vehicles, it was 85%, Pack-houses 99%, and ripening chambers 91%. This clearly shows that the focus should not be only on cold storage enablement but on cold chain development.
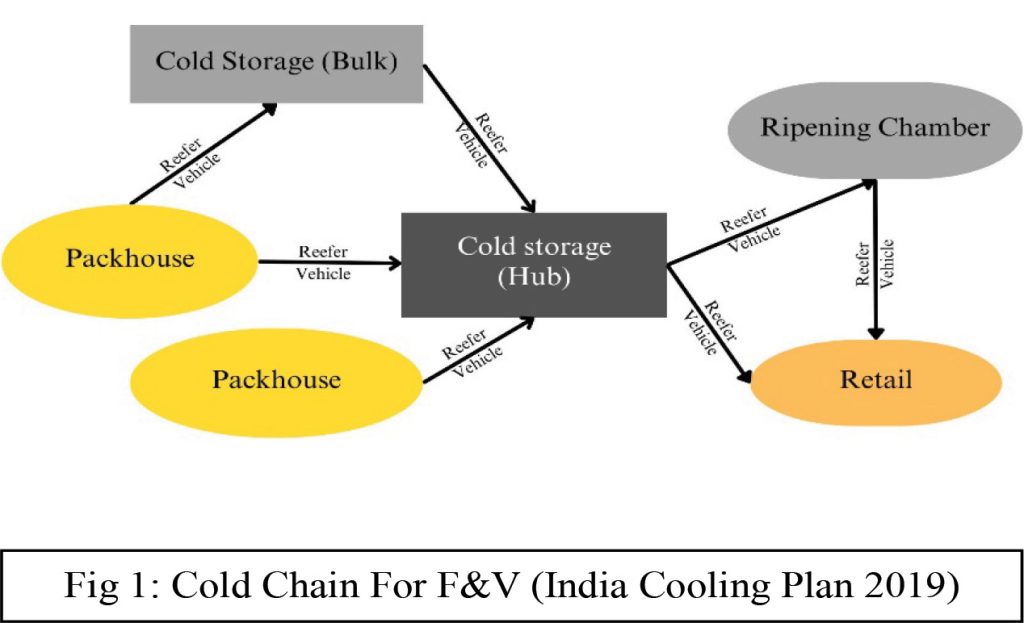
- Inefficient Transportation Systems: The transportation system plays a pivotal role in determining the quality of perishable goods. In many cases, inadequate transportation facilities, coupled with prolonged transit times, result in the deterioration of fruits and vegetables before they reach the market. Investing in refrigerated transport and improving logistical efficiency can address this challenge.
- Limited Value Addition: The lack of processing facilities for fruits and vegetables contributes to their higher vulnerability to spoilage. Processing levels in F&V currently stand at close to 2% (MOFPI, 2020). Value addition techniques such as drying, canning, and freezing help extend the shelf life of these perishable commodities, but their availability/ adoption is limited in many regions.
Technological Interventions to Address Post Harvest Losses:
| Technology | Role | Impact |
| Precooling Technologies | Precooling involves rapidly reducing the temperature of fruits and vegetables immediately after harvest to slow down physiological processes. | This process minimizes post-harvest losses during subsequent transportation and storage, ensuring that the produce retains its quality and nutritional content. |
| Cold Storage Facilities | Cold storage facilities play a pivotal role in extending the shelf life of perishable fruits and vegetables by maintaining optimal temperature and humidity. | By slowing the natural ripening process, these facilities significantly reduce post-harvest losses and enable a more gradual market release, ensuring produce reaches consumers in a fresh state. |
| Transportation Advancements | Innovations in transportation, including refrigerated trucks and containers, facilitate the seamless movement of perishable goods from farms to markets across vast distances. | Enhanced transportation prevents exposure to ambient conditions, reducing the risk of spoilage during transit. Upon reaching consumers, this ensures that fruits and vegetables maintain their quality and nutritional value. |
| Humidity Control Systems | Maintaining optimal humidity levels is crucial for preserving the texture and freshness of fruits and vegetables. | Humidity control systems in storage and transportation prevent wilting and decay, preserving the visual appeal and market value of the produce. |
| Smart Packaging Technologies | Smart packaging involves the integration of sensors and modified atmosphere technologies to monitor and control the storage environment within the packaging. | By providing real-time data on factors like temperature and humidity, smart packaging helps adjust storage conditions during transportation and retail, thereby further extending the freshness of fruits and vegetables. |
| Traceability Systems | Traceability technologies, such as barcodes and RFID tags, enable real-time tracking of fruits and vegetables throughout the supply chain. | Improved traceability enhances accountability and transparency, allowing for swift identification and removal of contaminated or spoiled batches, thus minimizing overall losses. |
| Data Analytics and Predictive Modelling | Advanced data analytics and predictive modelling tools analyse historical data and environmental conditions to forecast the shelf life and optimal storage requirements for specific fruits and vegetables. | This proactive approach enables better inventory management, reduces waste, and ensures that perishable items are brought to market precisely when they are at their peak freshness. |
Government Initiatives and Policies for Cold Chain
| a) Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY):
b) The INR 6000 Cr scheme focuses on creating modern infrastructure for efficient supply chain management, reducing losses from farm gates to retail. Operations Greens is majorly focused on F&V |
a) Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure Scheme: Started in 2008, it aids in creating integrated cold chain facilities, reducing losses, and supporting diverse produce | a) Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture:
b) Aiming for holistic horticulture growth, MIDH provides financial assistance for various activities, including the construction/modernization of cold storages. |
| • Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme for Cold Storage: Implemented by the National Horticulture Board, it offers credit-linked subsidies for the development of cold storage, addressing regional disparities and promoting horticulture storage. | a) Priority Sector Lending Norms: RBI covers loans for storage facilities, including cold storage, regardless of location, promoting financial support for infrastructure development. | a) NABARD Special Fund:
b) A dedicated INR 2000 Cr fund supports affordable credit for setting up, modernizing, and expanding food processing units, boosting the overall food processing sector. |
Market Trends and Future Outlook to address post-harvest losses:
Demand for Exotic and Specialty Produce
In India, the demand for exotic and specialty produce in fruits and vegetables is evident through the increasing popularity and consumption of items such as avocados, dragon fruit, kale, quinoa, asparagus, and various types of berries. These non-traditional fruits and vegetables, once considered exotic, are now regularly featured in upscale grocery stores and restaurants. The demand reflects a shift in consumer preferences toward diverse and globally inspired culinary experiences, driven by factors like health consciousness, changing lifestyles, and a willingness to explore new flavours and textures.
Rise in the sales of Processed F&VThough the penetration of processed F&V is comparatively lesser than Fresh produce, the category has shown a considerable amount of growth. The retail value sales of processed F&V in India increased by 11% to INR 22.4 billion in 2022, showcasing a significant growth in market value. Frozen processed fruit and vegetables, as the best-performing category, grew by 15% to INR 9.2 billion, contributing substantially to the overall sales increase (Euromonitor). Urban consumers, returning to busy lifestyles post-pandemic, have driven the demand for convenient and time-saving food products, including processed F&V. The preference for ready-to-eat or easy-to-prepare options aligns with the convenience offered by processed F&V, contributing to increased sales. Metal packaging, especially metal food cans, emerged as the best-performing type with a 6% growth to 102 million units. Metal cans provide necessary protection for shelf-stable fruit products (Euromonitor).
Emerging Favourites in Processed F&V Category:
The processed F&V category is one of the most value-driving categories in terms of exports. Processed fruits exports in 2022-23 were valued at 908.09 USD Million, and Processed vegetables export value was 508.97 USD Million.
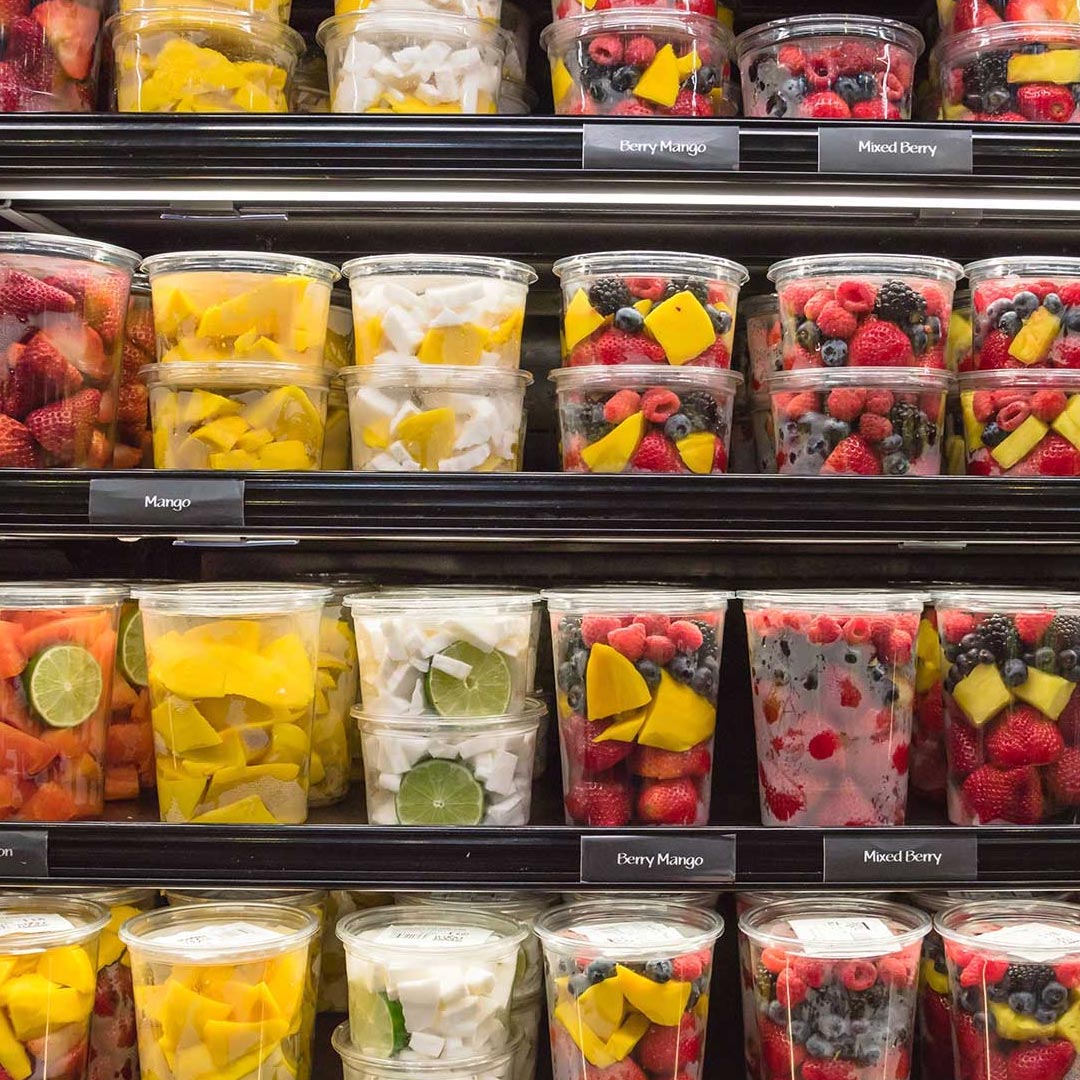

Pre-cut F&V
In India, the pre-cut fruits and vegetables market has witnessed remarkable growth due to urbanization and changing consumer lifestyles. This trend is fuelled by increased convenience, time-saving appeal, and a rising awareness of hygiene. Key players leverage advanced packaging and distribution networks, contributing to the expanding popularity of pre-cut F&V products.
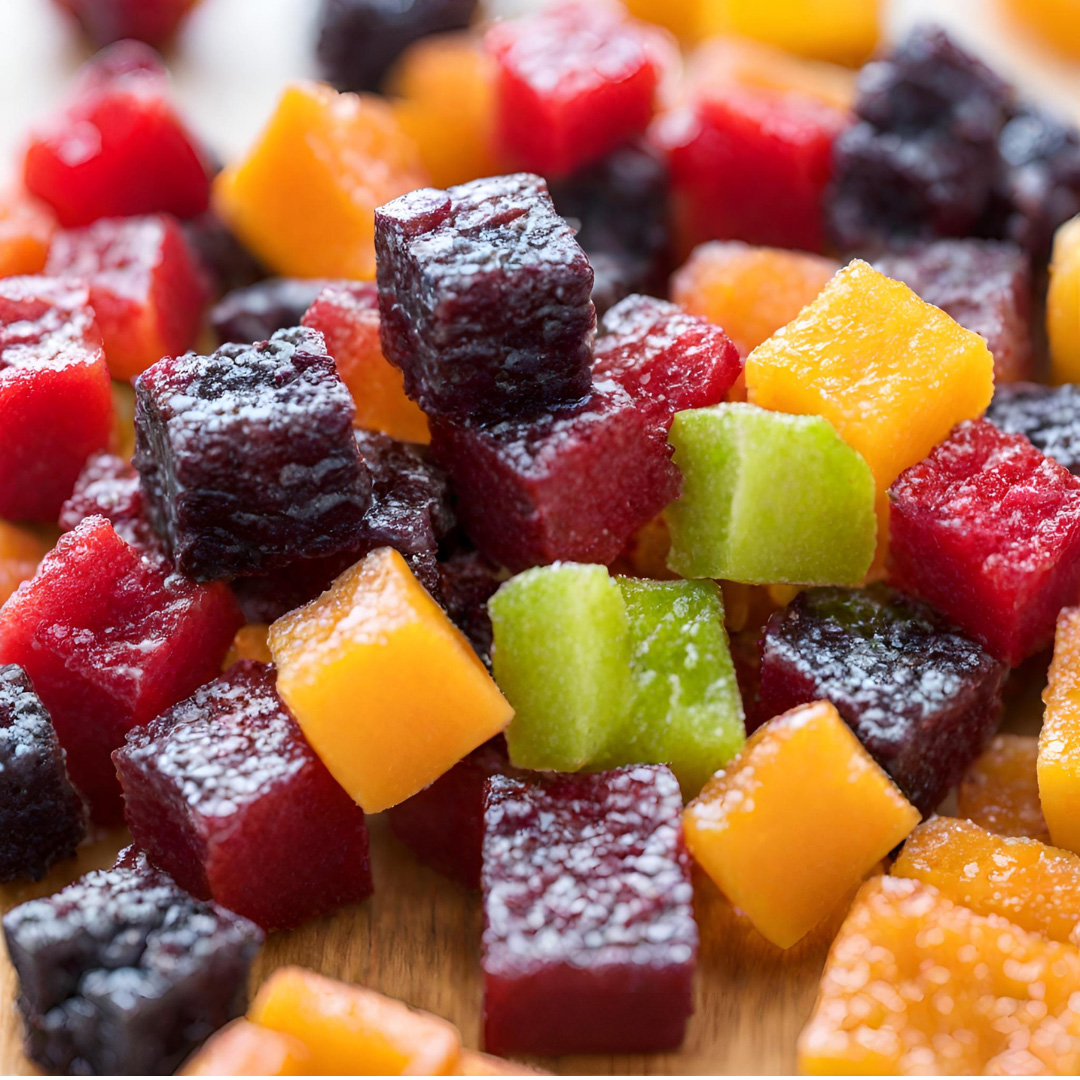

Seasoned, preserved, no-sugar fruit bites
Seasoned, preserved, no-sugar fruit bites represent a health-conscious snack revolution. These are preferred due to natural sweetness with a burst of flavours. Packed with nutrients, these bites redefine snacking, offering guilt-free indulgence without compromising on taste. A fusion of innovation and wellness, they cater to the modern consumer’s discerning palate.
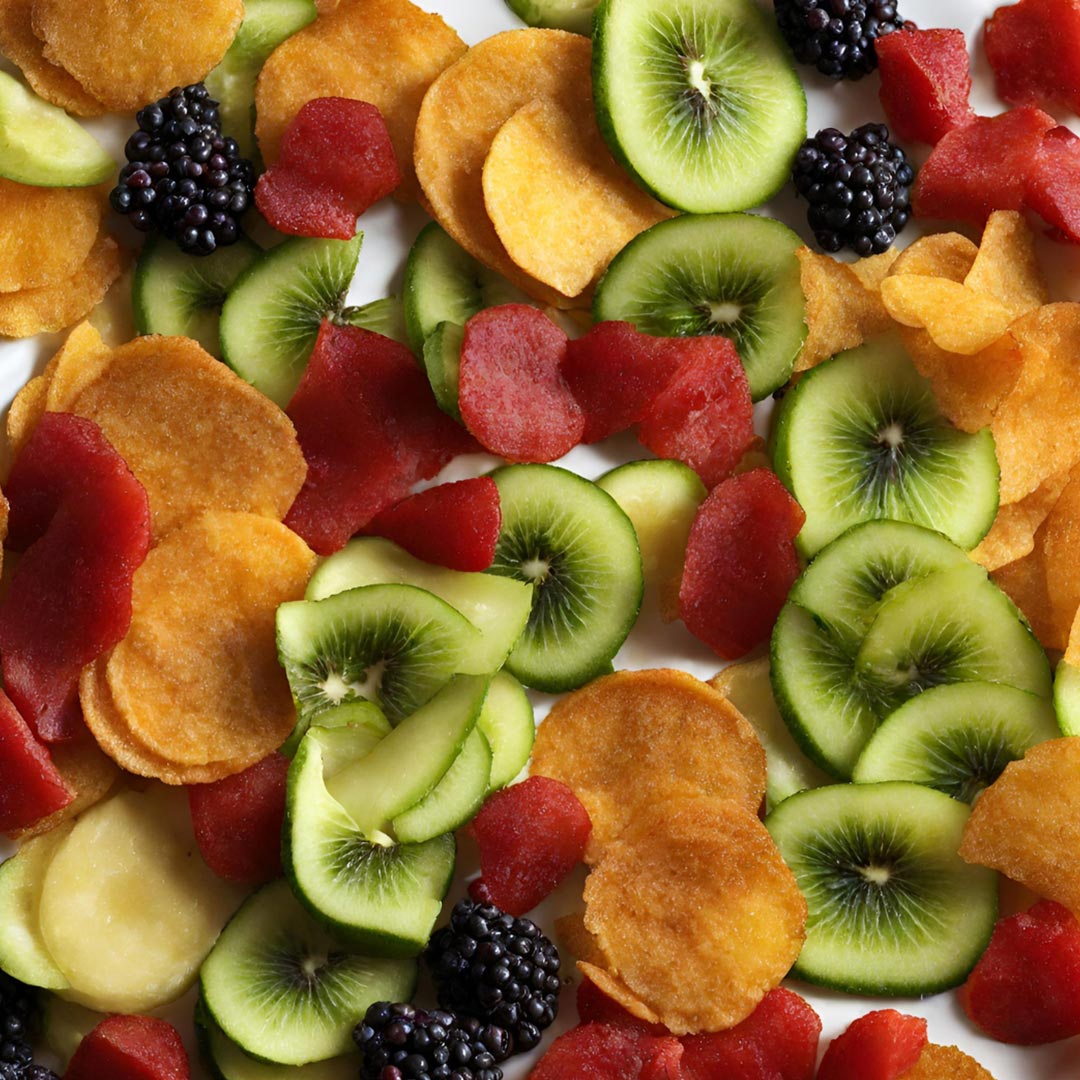

F&V Chips (non-fried)
These chips are typically crafted through innovative dehydration or baking methods and vacuum fried, preserving the natural flavours and nutrients of the produce. As the popularity of non-fried F&V chips rises, manufacturers are exploring diverse flavours profiles, textures, and packaging innovations to capture the attention of a discerning and health-savvy consumer base.
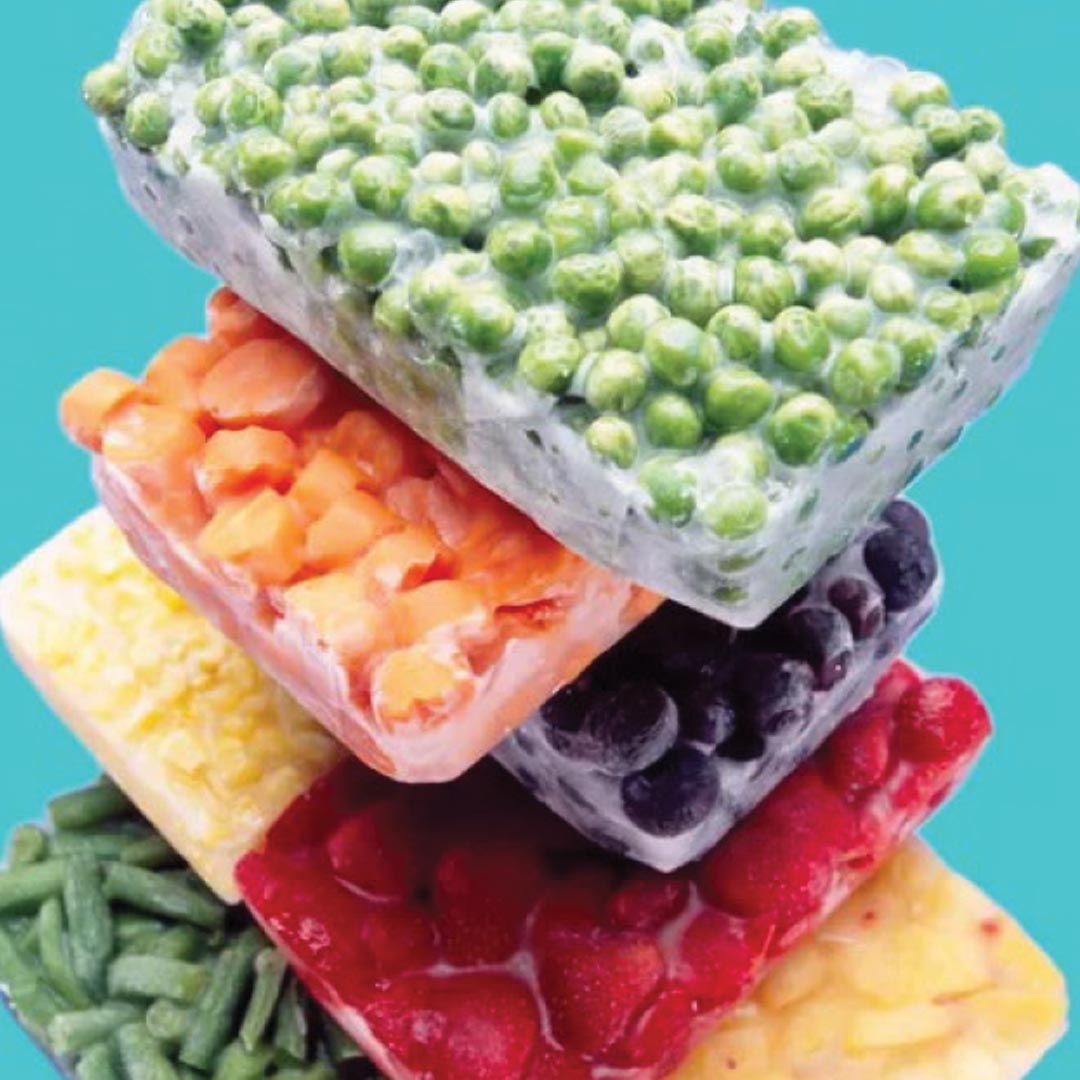

Frozen F&V
The freezing process effectively preserves the nutritional value of fruits and vegetables, offering consumers a convenient alternative to fresh produce with an extended shelf life. In recent years, the frozen F&V market has witnessed a surge in innovation, with manufacturers introducing a diverse array of products such as pre-cut, mixed blends, and exotic fruit varieties. Bulk packs are extensively used in the B2B industry due to year-round availability and convenience.
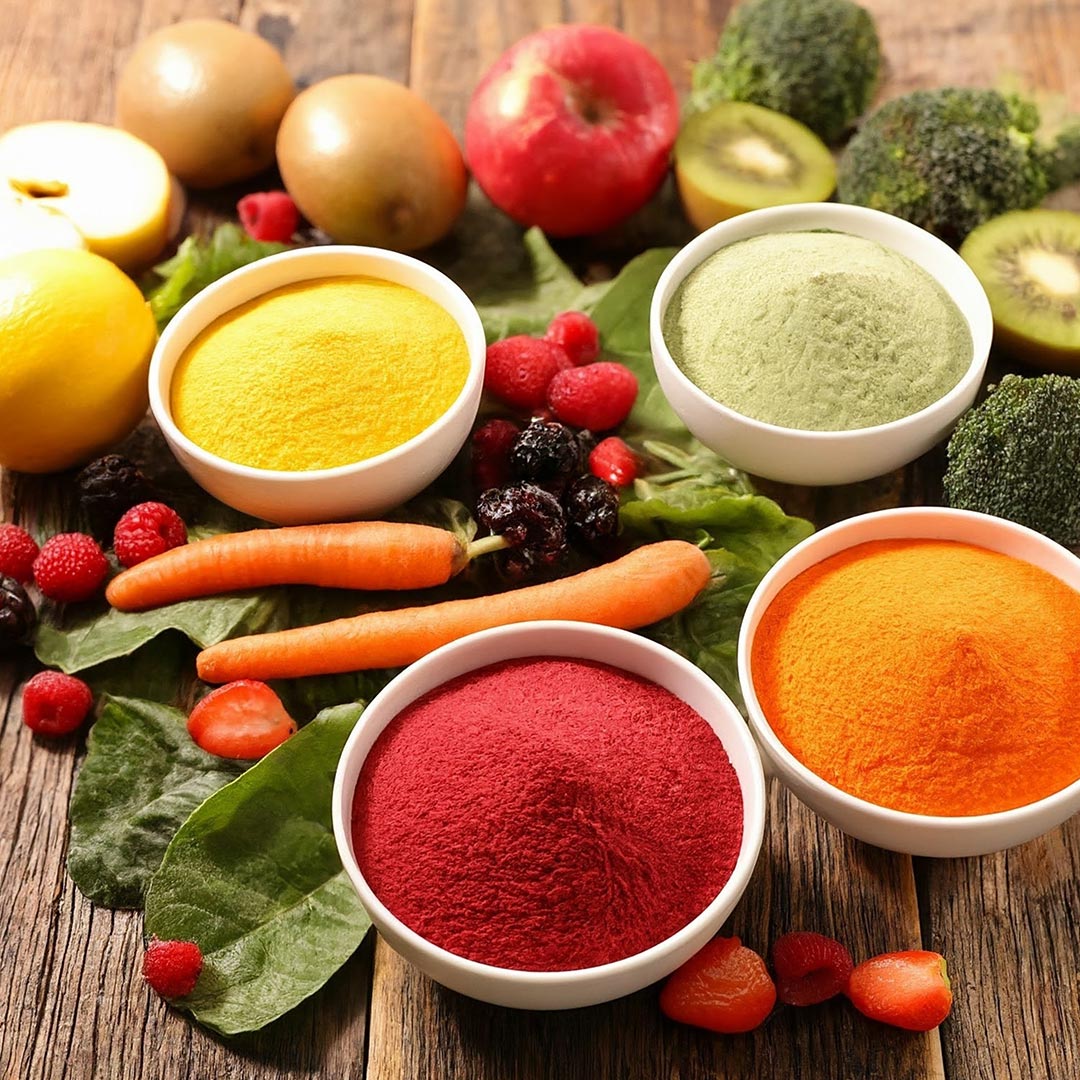

F&V Powders
These powders are created through a dehydration process that retains much of the original produce’s flavours, colour, and nutritional content. The resulting product is a concentrated form of fruits and vegetables that can be easily integrated into a diverse range of applications, including beverages, snacks, and supplements. Their long shelf life and ease of transportation make them an attractive option for manufacturers seeking innovative and health-conscious ingredient solutions in the ever-evolving food and beverage market. Due to its ease of incorporation, powder forms are in huge demand in B2B and service industries.
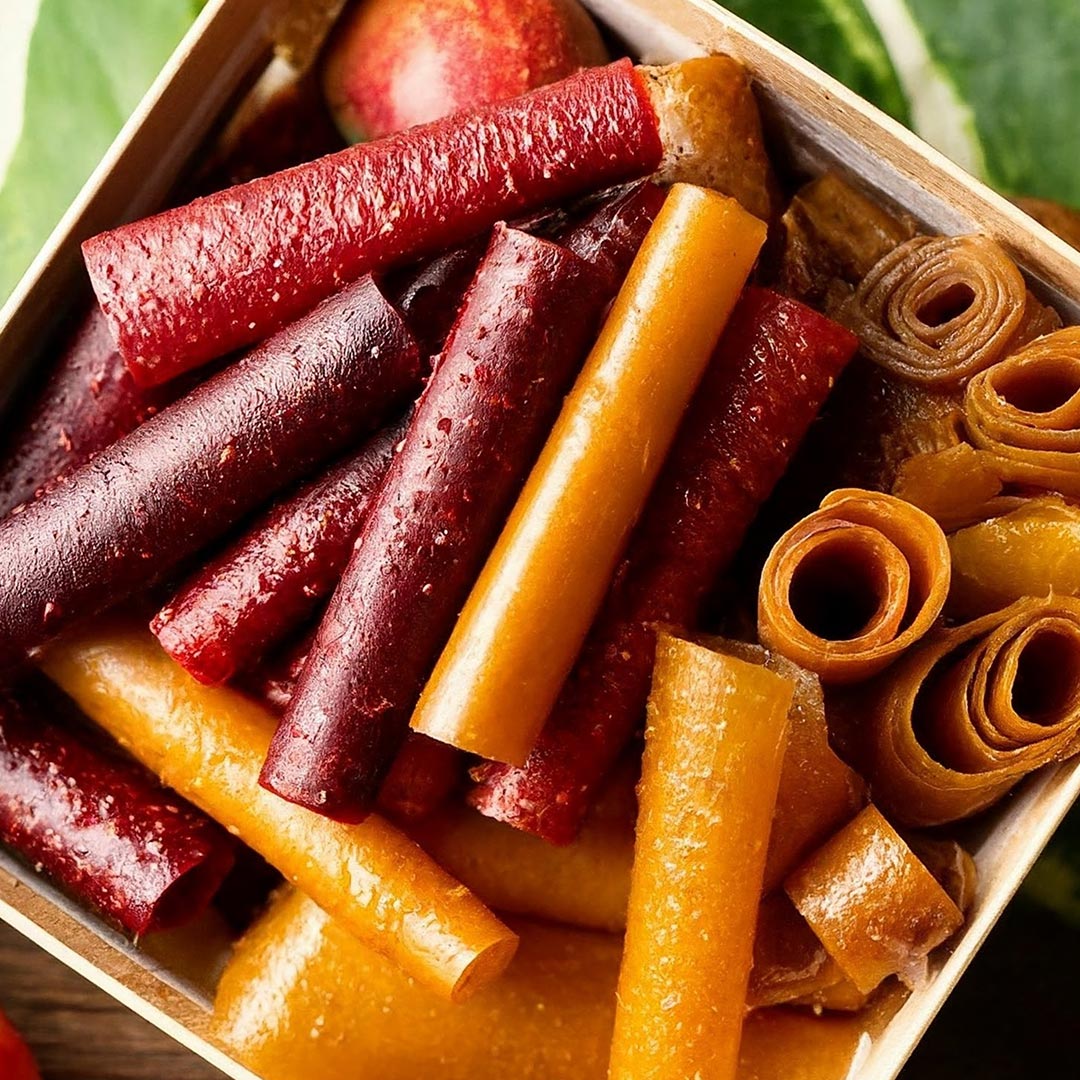

Fruit Leathers
Fruit leathers, also known as fruit strips or fruit rolls, are a popular and convenient snack option derived from pureed and dehydrated fruits. Typically, fruit leathers are made by blending fruits into a puree, spreading the mixture thinly, and then dehydrating it to remove moisture, resulting in a flexible, chewy texture. The product appeals to health-conscious consumers seeking natural alternatives to traditional snacks, as it often contains no added sugars or preservatives.
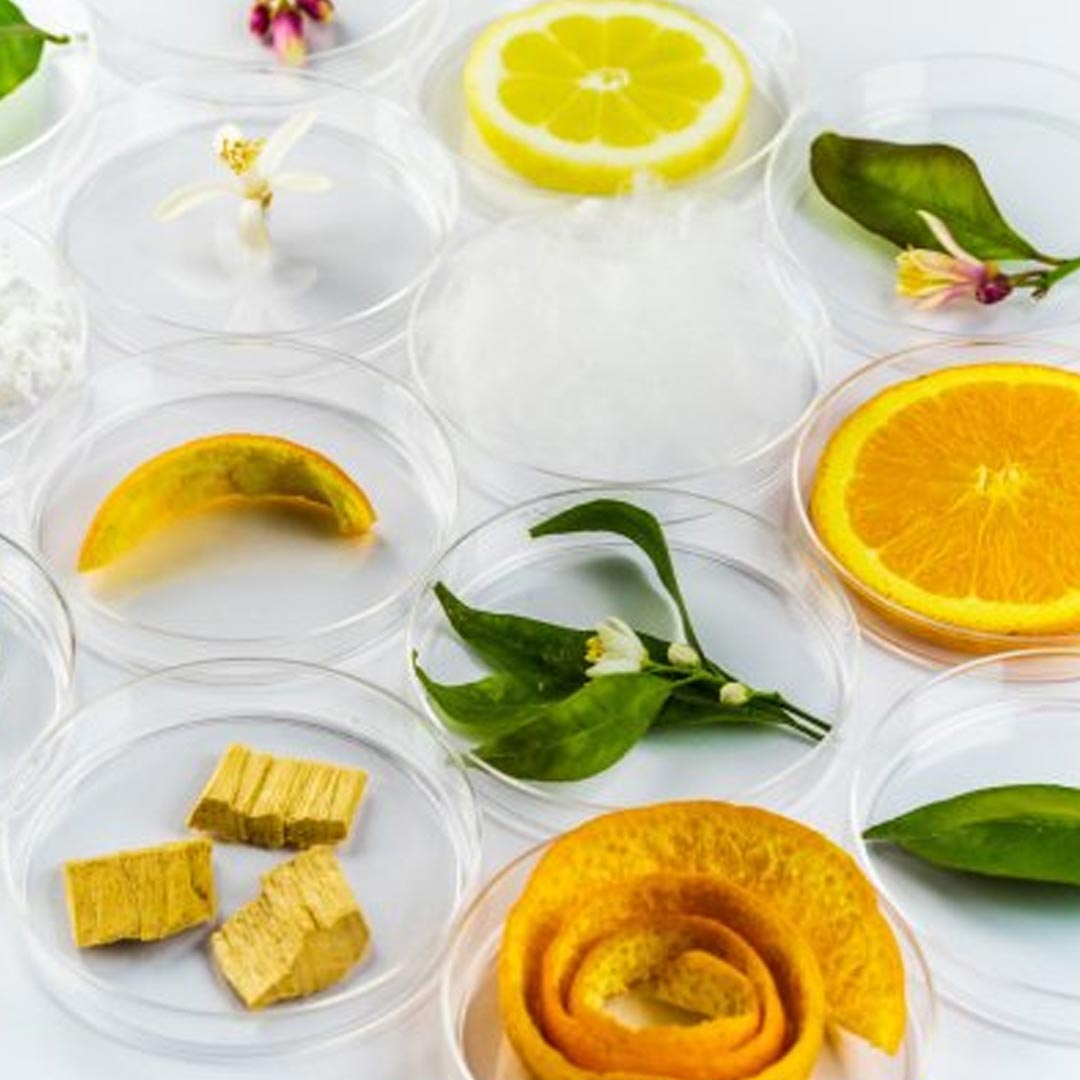

Upcycled Peel products
Upcycled Peel products represent an innovative and sustainable approach to reducing food waste and promoting environmental consciousness. These include powders, chips, and infused teas.
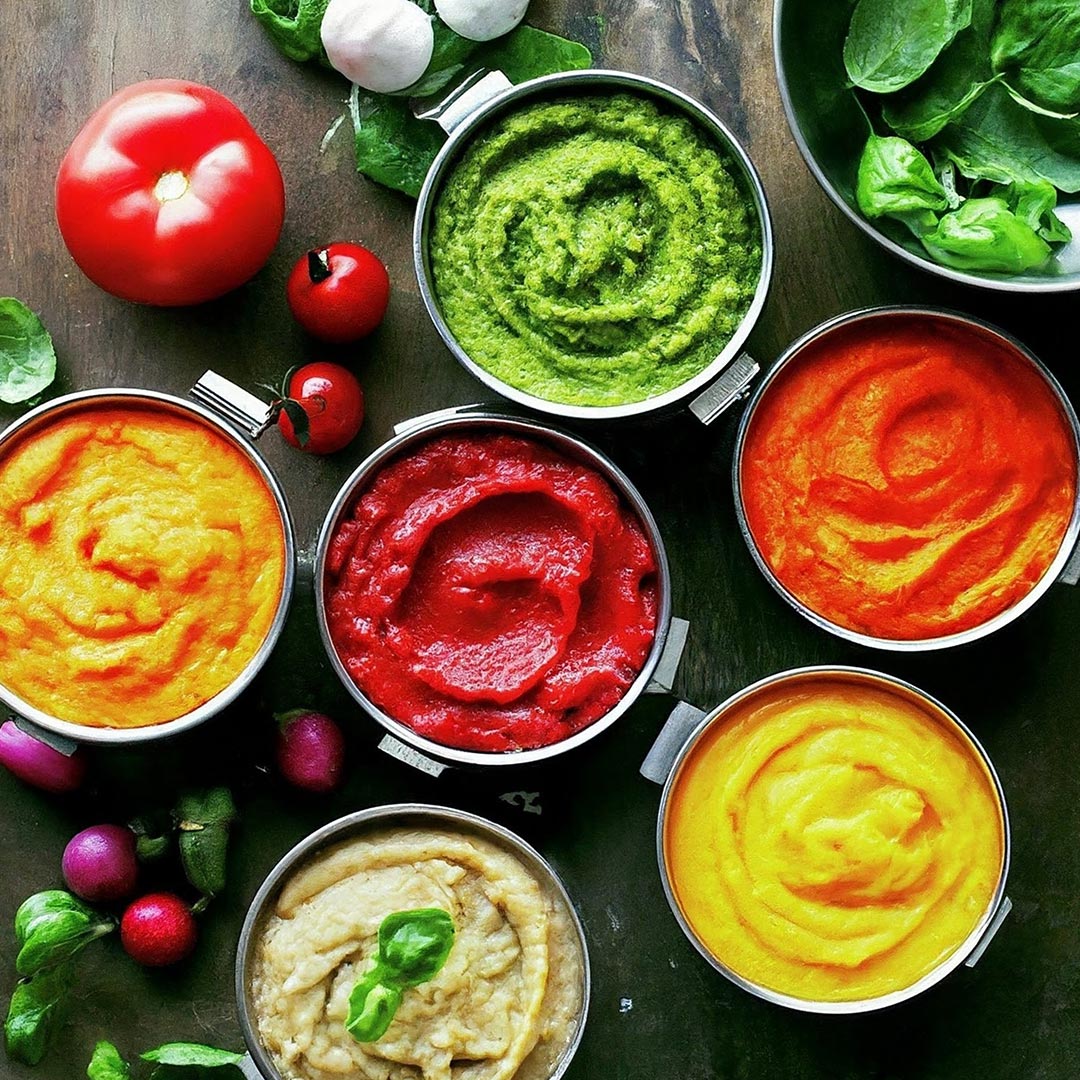

Vegetable pastes
Vegetable pastes offer convenience, flavours, and nutritional benefits. These pastes, derived from a variety of vegetables, undergo a processing method to transform raw ingredients into concentrated, easily usable forms. With an emphasis on natural ingredients and minimal processing, vegetable pastes cater to health-conscious consumers seeking wholesome alternatives. Vegetable pastes also cater to the B2B industry, since the pre-processed product makes it convenient to mix in any recipes.
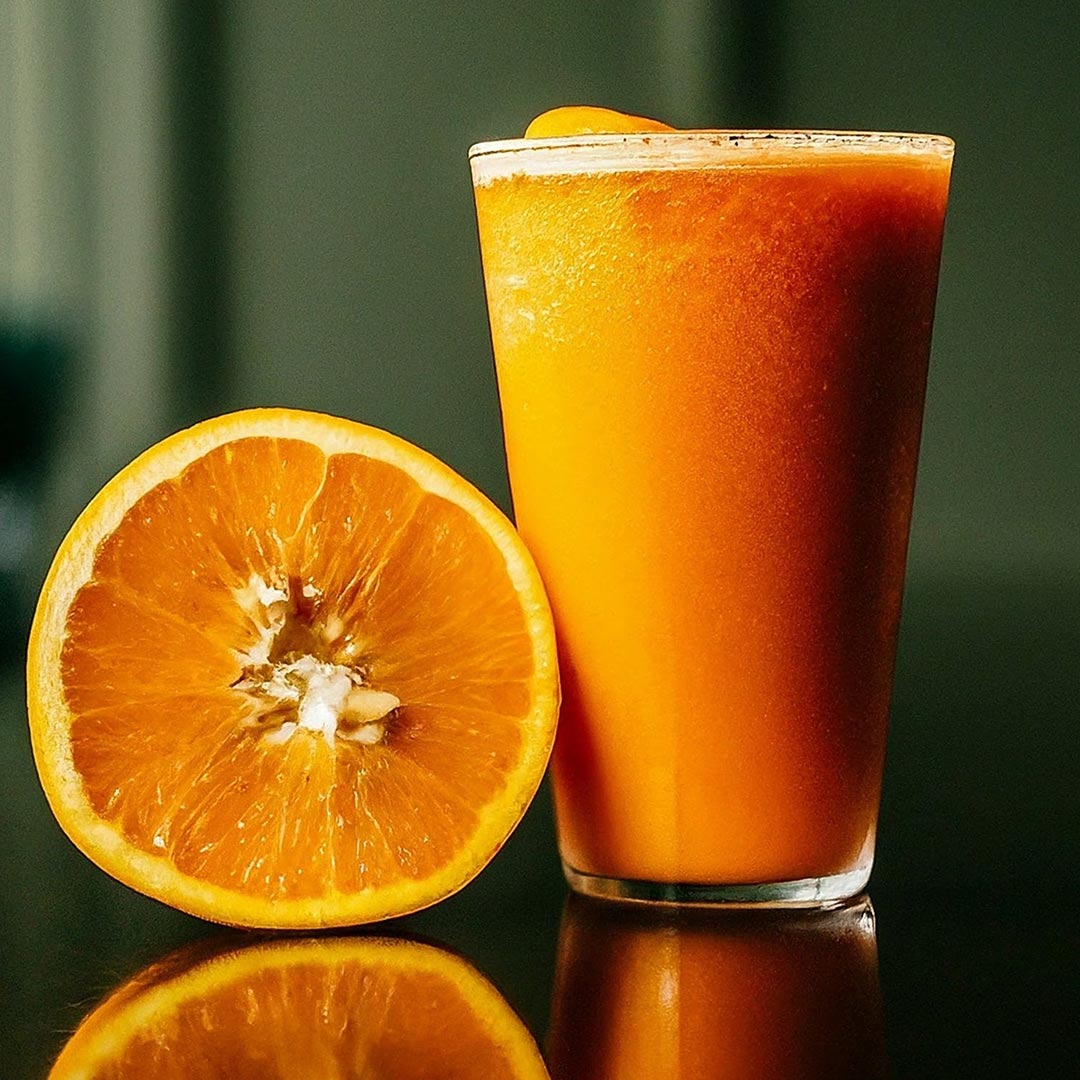

Fruit Pulps and concentrates
Fruit leathers, also known as fruit strips or fruit rolls, are a popular and convenient snack option derived from pureed and dehydrated fruits. Typically, fruit leathers are made by blending fruits into a puree, spreading the mixture thinly, and then dehydrating it to remove moisture, resulting in a flexible, chewy texture. The product appeals to health-conscious consumers seeking natural alternatives to traditional snacks, as it often contains no added sugars or preservatives.
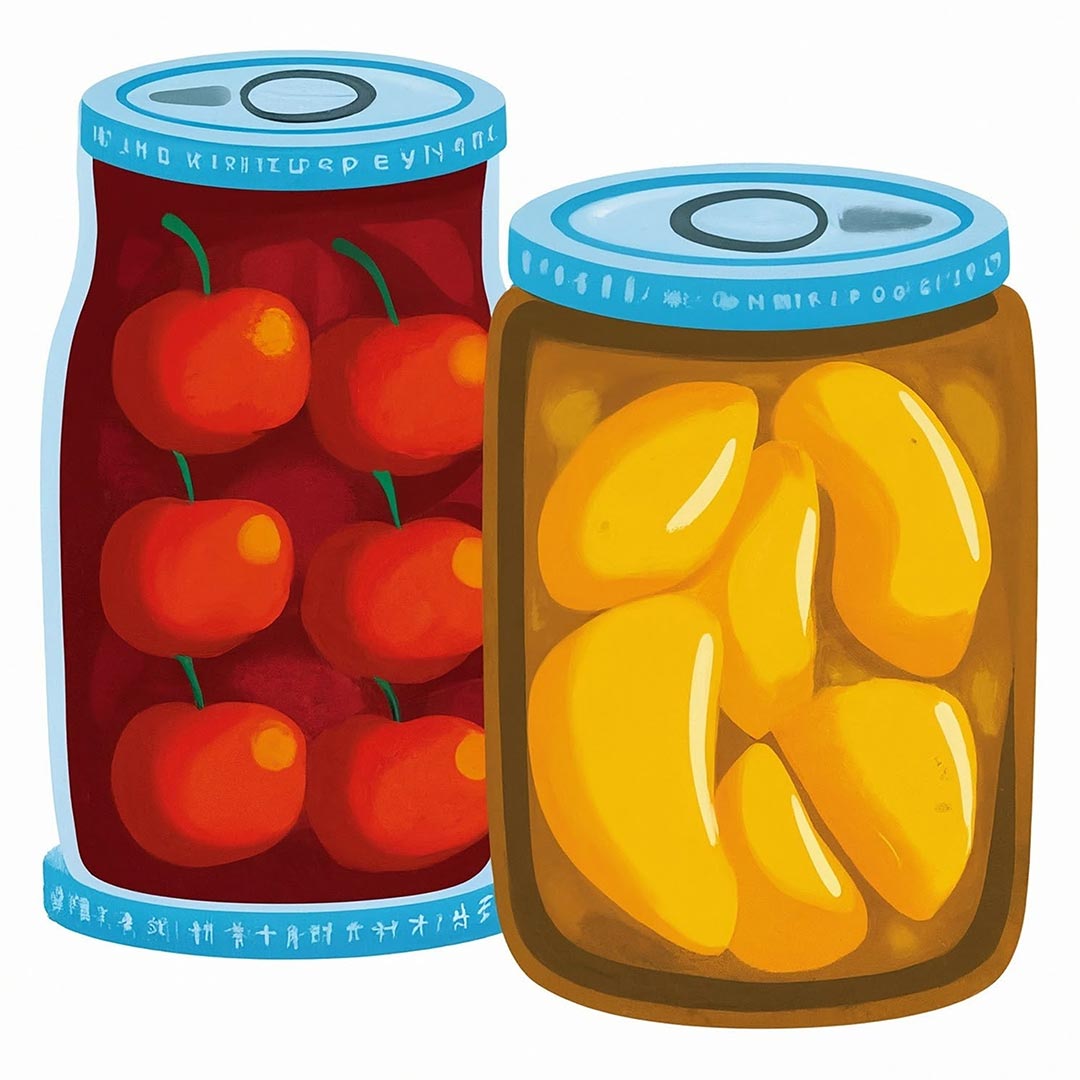

Canned F&V
The canning process involves retort processing of fruits and vegetables in airtight containers, effectively inhibiting bacterial growth and enzymatic activity. This preservation method ensures year-round availability of the produce.
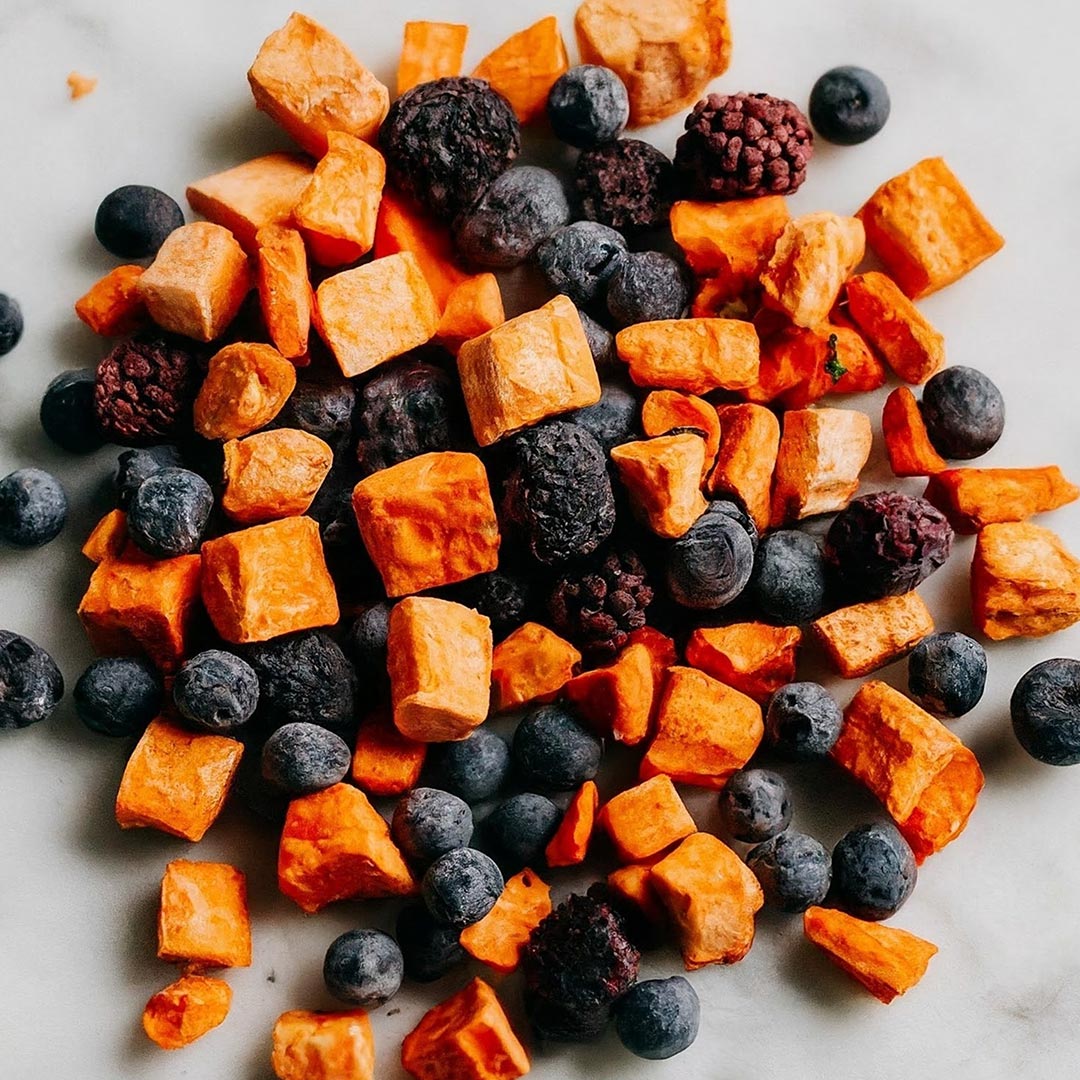

Freeze-dried F&V
Freeze-drying, a method of preserving fruits and vegetables, involves removing moisture at low temperatures to maintain nutritional integrity and enhance shelf life. This process results in lightweight, crispy, and easily rehydratable products that retain much of their original flavours, colour, and nutrients. Freeze-dried fruits and vegetables have gained popularity due to their convenience, extended storage capability, and minimal nutrient loss compared to traditional drying methods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing post-harvest losses in India’s fruit and vegetable industry demands a comprehensive strategy. The challenges of post-harvest losses and inefficiencies in the post-harvest process highlight the need for improved cold chain infrastructure, transportation systems, and value-addition techniques. Technological interventions, such as cold storage facilities, transportation advancements, and smart packaging, offer promising solutions. Sustained efforts, continued innovation, and effective implementation of policies are essential to truly address and reduce post-harvest losses in India.
Minimizing post-harvest losses in fruits and vegetables is crucial for enhancing health and nutrition in India. Reduced losses mean more produce reaching consumers, addressing malnutrition issues. Additionally, it promotes sustainability by conserving resources invested in cultivation. Lower wastage reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with decomposing organic matter, contributing to a healthier planet. Efficient post-harvest practices thus play a pivotal role in improving both public health and environmental sustainability in India.
Author:

Associate Consultant – Food Processing and Retail practice
Connect with Author at: E-mail foodbiz@sathguru.com
 Grow Beyond
Grow Beyond