Navigating Digital Transformation for R&D Organization in Seed Industry
Introduction
The journey of digital transformation for R&D organization in a seed industry is unique. It involves not only the adoption of new technologies but also a cultural shift towards innovation and data-driven decision-making across every unit that contributes to the R&D process (Biotech, Breeding, Product Development (PD), Commercialization). As leaders in this specialized area, the transition through the six stages of digital transformation must be approached methodically, ensuring that the organization’s core mission of developing high-yield, resilient varieties remains at the forefront. In this article, we will explore how an R&D organization in the seed industry can navigate each stage of digital transformation, providing a comprehensive guide for leaders.
Why Seed R&D needs to navigate through Digital Transformation
In the increasingly competitive and rapidly evolving field of agriculture, seed research and development (R&D) organizations face a pressing need to embrace digital transformation. This necessity extends equally to Product Development (PD), as both departments are critical links in the same chain, much like a relay race where both runners need to maintain the same pace for success.
Leveraging digital transformation allows for the integration of vast data from genomic information, field trials, and market insights. Advanced analytics and machine learning can process this data to yield insights that guide smarter, evidence-based decisions in both R&D and PD. This is crucial for predicting crop performance, optimizing breeding strategies, and tailoring product development to market needs. It also enables meticulous planning and management of resources, crucial for coordinating field trials and product testing locations across key markets. Using geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing, organizations can optimize environmental conditions and resource allocation, essential for both the R&D and PD processes. It further enhances efficiency in using human and material resources. Automation and robotics can reduce labor-intensive tasks in field trials and labs, while IoT devices can monitor crop health and soil conditions in real-time, improving input efficiency like water and fertilizer usage. This streamlining is essential for both R&D and PD to focus more on innovation and less on routine tasks.
By adopting digital strategies, seed R&D and PD can accelerate the development and deployment of high-quality hybrid seeds. Digital integration ensures that every step from gene discovery to market launch is streamlined, reducing time-to-market and ensuring that superior seed varieties meet market needs swiftly.
The Evolutionary Stages of Digital Transformation: From Digitization to Digitally Enabled Business Models
The digital transformation journey encapsulates three critical phases: digitization, digitalization, and the adoption of digitally enabled business models. Digitization marks the initial phase, where analog information is converted into digital formats, allowing data to be more easily captured, stored, and analyzed. This foundational step enhances efficiency and opens the door to new ways of processing and managing information. Progressing to digitalization, organizations re-engineer and optimize their processes using digital technologies, not just converting data but transforming how business operations are conducted, leading to improved workflows, increased productivity, and the ability to make data-driven decisions. The culmination of this journey is the development of digitally enabled business models, where digital technologies are leveraged to create new value propositions, innovate products and services, and redefine interactions with customers and the market. This evolutionary path not only revolutionizes internal processes but also reshapes industry landscapes, enabling organizations to stay competitive and responsive to rapidly changing market dynamics and consumer expectations.
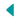
Strategic Roadmap
The strategic roadmap for digital transformation in a seed industry R&D organization is divided into six detailed stages, each representing a step change in the integration of digital technology and practices.
Stage 1: Business as Usual
In Stage 1 of digital transformation, an R&D organization operates with entrenched traditional methodologies. Manual data collection and analysis predominate, with research largely driven by empirical knowledge and physical trials. For instance, a company might rely on handwritten notes for documenting cross-breeding results or use basic Excel spreadsheets for tracking plant growth data without harnessing the power of data analytics.
Leadership action during this initial phase involves awakening the organization to the possibilities of digital enhancement without overwhelming the team. A practical example could be introducing a simple database management system to replace paper logs, allowing for easier data retrieval and analysis. This change not only streamlines record-keeping but also minimizes errors associated with manual entry. It further benefits in IP management to safeguard valuable genetic information, streamline patent management and ensure compliance with global IP regulations. This protection is vital across both R&D and PD to secure innovations and facilitate the legal sharing of genetic resources.
Leaders should also showcase successful digital adoption stories within the seed R&D sector. An example is a peer organization that transitioned to digital phenotyping, using image capture and analysis software to monitor plant development more accurately and efficiently than traditional visual assessments. By highlighting these real-world applications, leaders can illustrate the tangible benefits of digital tools, encouraging a shift in mindset and preparing the ground for more comprehensive digital strategies in the future stages.
Stage 2: Present and Active
In Stage 2, an R&D organization begins to tentatively embrace digital technologies. Initial experiments with digital tools are scattered across various teams, demonstrating potential benefits but lacking a coordinated approach. For example, one team might start using GPS mapping for precise field trial layouts, while another experiments with basic drone imagery to assess crop health from above. These efforts, though innovative, often operate in isolation without contributing to a broader digital strategy.
Leadership action is crucial to channel these individual initiatives into a cohesive digital transformation effort. Establishing a centralized ‘Innovation Hub’ serves as a critical step, acting as a melting pot for ideas and best practices. This hub can foster collaboration, allowing teams to learn from each other’s successes and challenges. For instance, the GPS mapping team could share insights on data accuracy improvements, while the drone imagery group might demonstrate how aerial photos can detect plants under stress (due to biotic or abiotic factors)..
To further embed digital practices, leaders should introduce training sessions focused on data literacy and digital tool utilization, tailored to the specific needs of seed R&D. Highlighting a case study, such as a competitor’s successful integration of a cloud-based data platform for real-time trial analysis, can serve as motivation. These examples not only inspire teams but also illustrate the practical application and benefits of digital tools, encouraging broader adoption across the organization.
Stage 3: Formalized
By Stage 3, the seed industry R&D organization has moved beyond initial experiments with digital technologies to embrace a more structured approach to digital transformation. Efforts become standardized and aligned with the organization’s broader goals. For example, the integration of a comprehensive data management system enables seamless tracking and analysis of genetic information, trial results, and environmental conditions across multiple research sites.
Leadership action during this phase focuses on embedding digital initiatives into the fabric of the organization’s strategy. The establishment of a digital transformation office or team is pivotal. This group is tasked with overseeing the implementation of digital projects, ensuring they align with research objectives, and measuring their impact. An illustrative example would be adopting a cloud-based platform for collaborative genetic sequencing analysis, allowing scientists across different locations to share insights and findings in real time, thus speeding up the breeding process for new varieties.
To further formalize digital adoption, the organization might partner with technology providers specializing in agricultural analytics or genomic data processing. Such partnerships can offer customized solutions and training, tailored to the unique needs of seed research. A real-world example includes a seed company collaborating with a software firm to develop a machine learning model that predicts a hybrid’s performance based on genotypic, phenotypic and environmental data.. This partnership not only enhances the company’s breeding programs but also serves as a benchmark for digital innovation in the sector.
During this stage, leaders must ensure that there is clear communication about the benefits and progress of digital projects, fostering an environment of transparency and engagement. By formalizing digital initiatives and demonstrating their value, the organization sets a solid foundation for more advanced digital integration in subsequent stages.
Stage 4: Strategic
In Stage 4 of the digital transformation journey, a seed R&D organization strategically embeds digital tools and analytics into its core processes. This stage marks a significant shift, with digital initiatives becoming central to the organization’s research strategy, facilitating cross-functional collaboration and data-driven decision-making.
Leadership action is focused on building a robust infrastructure that supports advanced digital capabilities. This includes upgrading IT systems to handle large-scale data analytics, ensuring high-speed connectivity for seamless data access across research sites, and implementing secure cloud storage solutions for collaborative projects.
An example of strategic digital integration could be the deployment of an integrated platform that combines genomic data, environmental factors, and phenotypic data. This platform enables researchers to simulate breeding outcomes using predictive models, significantly accelerating the development of new varieties. Another example is the use of sensor networks in field trials to collect real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, and crop health. This data can be integrated with statistical tools and other environmental information to optimize trial locations, thereby enhancing resource efficiency. By carefully selecting sites that maximize the quality of results based on environmental suitability, organizations can improve yield predictions and accelerate the developmental timeline. This strategic use of technology not only optimizes the use of resources but also improves the quality of research outcomes, ultimately leading to a faster time-to-market for new hybrids.
To ensure the success of these strategic initiatives, leaders must foster a culture of innovation and continuous learning. This could involve organizing hackathons to explore new digital solutions, offering professional development courses in data science and bioinformatics, and establishing partnerships with tech companies to gain access to cutting-edge tools and expertise.
Showcasing a success story, such as a collaboration with a technology firm that resulted in the development of an AI-driven disease detection system for crops, can illustrate the tangible benefits of strategic digital integration. By prioritizing strategic digital initiatives, the organization not only enhances its research capabilities but also positions itself as a leader in the digital transformation of the seed industry.
Stage 5: Converged
By Stage 5, the seed R&D organization has fully integrated its digital and operational strategies, achieving a seamless convergence of technology and research processes. Digital transformation is no longer a separate initiative but a core component of the organization’s DNA, driving innovation and efficiency across all facets of R&D.
Leadership action at this stage is crucial in ensuring that digital tools and data analytics are embedded in everyday breeding, research and trialling activities. Leaders must oversee the development of an intuitive, user-friendly digital ecosystem that supports researchers in their daily tasks. This involves not just implementing technology but also ensuring it is accessible and adds real value to the R&D process.
An illustrative example of this stage could be the creation of a digital twin for crop development, allowing researchers to simulate and predict plant growth under various environmental conditions without the need for extensive physical trials. Another example is the adoption of a comprehensive digital supply chain management system that tracks seed development from breeding through to commercial production, ensuring traceability and efficiency.
To foster an environment where such advanced digital practices become the norm, leaders should emphasize continuous training and professional development. Encouraging cross-disciplinary teams and facilitating knowledge exchange between data scientists and plant biologists can spur innovative solutions to research challenges.
Highlighting a case where converged digital strategies have led to breakthroughs, such as using machine learning algorithms to uncover new genetic markers for drought resistance(Click here for Reference), can serve as a powerful testament to the value of digital integration. By reaching Stage 5, the organization not only solidifies its position as a frontrunner in digital adoption within the seed industry but also sets a benchmark for how technology can revolutionize seed R&D.
Stage 6: Innovative and Adaptive
In Stage 6, the R&D organization stands at the forefront of digital innovation. Having fully integrated digital technologies into its core processes, the organization now focuses on continuous innovation and adaptation to maintain its competitive edge. This stage is characterized by a proactive approach to exploring and implementing emerging technologies, ensuring the organization remains agile and responsive to new opportunities and challenges.
Leadership action is centered around fostering a culture of perpetual innovation. Leaders must encourage experimentation and risk-taking, providing teams with the resources and freedom to explore new digital solutions. This includes setting aside budgets for innovation projects, creating incubator programs for promising ideas, and establishing strategic partnerships with tech startups and academic institutions.
Examples of innovation in this stage might include leveraging CRISPR technology for precise gene editing, supported by AI-driven predictive models to anticipate the outcomes of genetic modifications. Another example is the use of advanced sensors and IoT devices in phenotyping, enabling the automatic collection and analysis of plant growth data under various environmental conditions.
To inspire continuous advancement, showcasing success stories is crucial. An example could be a breakthrough in increasing crop yield resilience to climate change, achieved through a combination of gene editing and data analytics to predict plant performance. Similarly, the implementation of blockchain technology for secure, transparent tracking of the seed development process from lab to market can illustrate the organization’s commitment to innovation and integrity.
By embracing Stage 6, the organization not only cements its position as a leader in digital transformation within the seed industry but also contributes to the broader goal of sustainable agriculture. Leaders play a key role in ensuring that the organization remains adaptable, leveraging digital innovation to address the pressing challenges of food security and environmental sustainability.
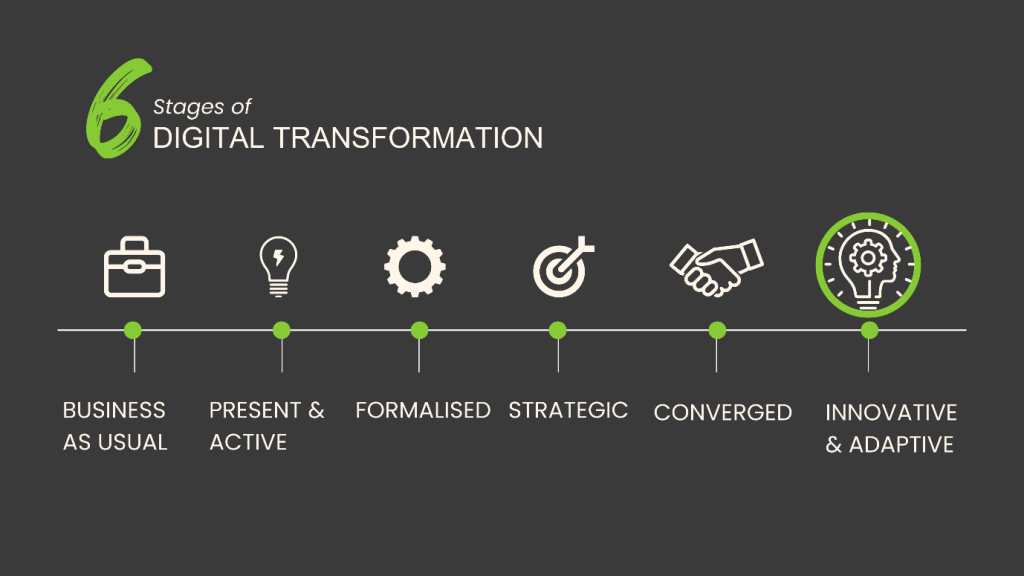
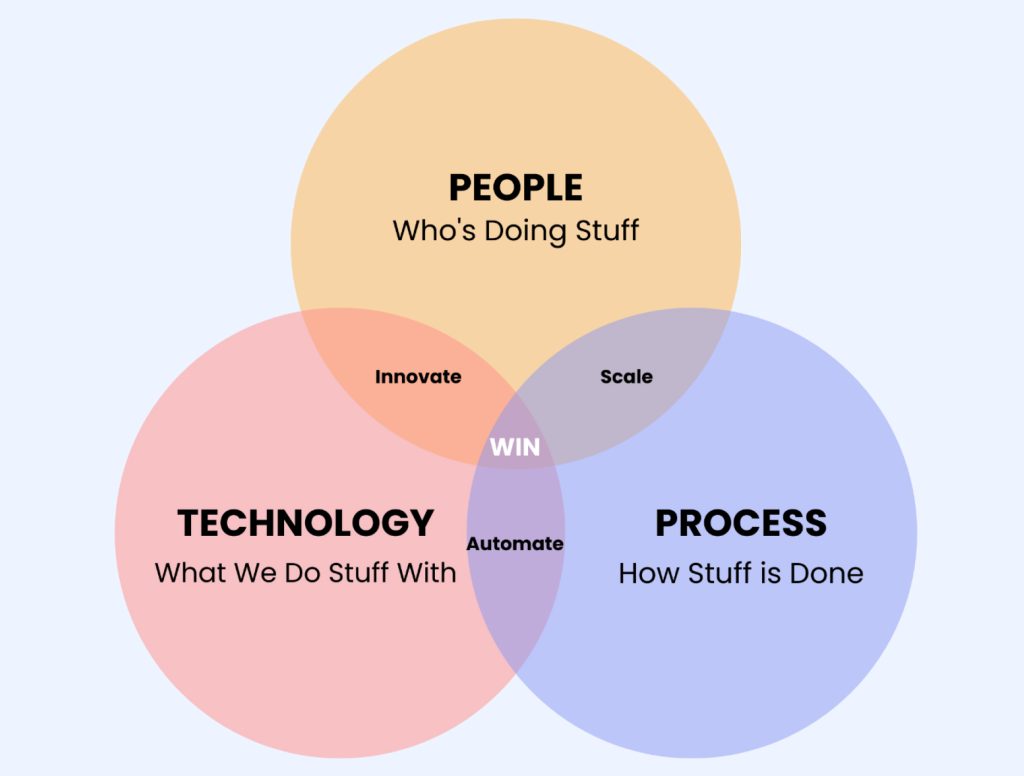 The Holy Trinity: People, Process and Technology
The Holy Trinity: People, Process and Technology
In the seed R&D sector, the successful execution of digital transformation hinges on the synergistic interplay of people, processes, and technology. People are the heart of transformation, requiring a shift in mindset to embrace new digital tools and methodologies. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and innovation, organizations empower their teams to adapt and thrive in a digitally evolving landscape. Processes must be reimagined and streamlined to leverage digital capabilities, ensuring that workflows are efficient, data-driven, and conducive to rapid experimentation and iteration. Finally, technology acts as the enabler, providing the infrastructure, tools, and platforms necessary to support advanced research activities, data analysis, and collaboration. Together, these elements create a robust framework for digital transformation, enabling seed R&D organizations to accelerate their research, enhance product development, and ultimately contribute to sustainable agricultural advancements.
Conclusion
In summary, the journey of digital transformation in a seed R&D organization is a structured yet flexible path that encompasses embracing technology, cultivating innovation, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Leadership is key in steering the organization through this journey, from initial digital awareness to becoming a beacon of innovation in the industry. By strategically navigating through the six stages of transformation, organizations can unlock significant advancements in seed research and development, contributing to more resilient and sustainable agricultural practices. The success of this journey hinges on the seamless integration of digital technologies with core R&D processes, ultimately enhancing the global quest for food security and agricultural sustainability.
Author:

Sr. Consultant – Digital Transformation
Connect with Author at: E-mail agribusiness@sathguru.com
 Grow Beyond
Grow Beyond