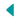
Increasing Relevance of Hydroponics
Among technologies that can potentially influence the future of agriculture and seed industry, hydroponics is one of the most exciting. The fact that hydroponics is prominently featuring in recent seed conferences in Netherlandsi is an indication of the potential and importance of the technology.
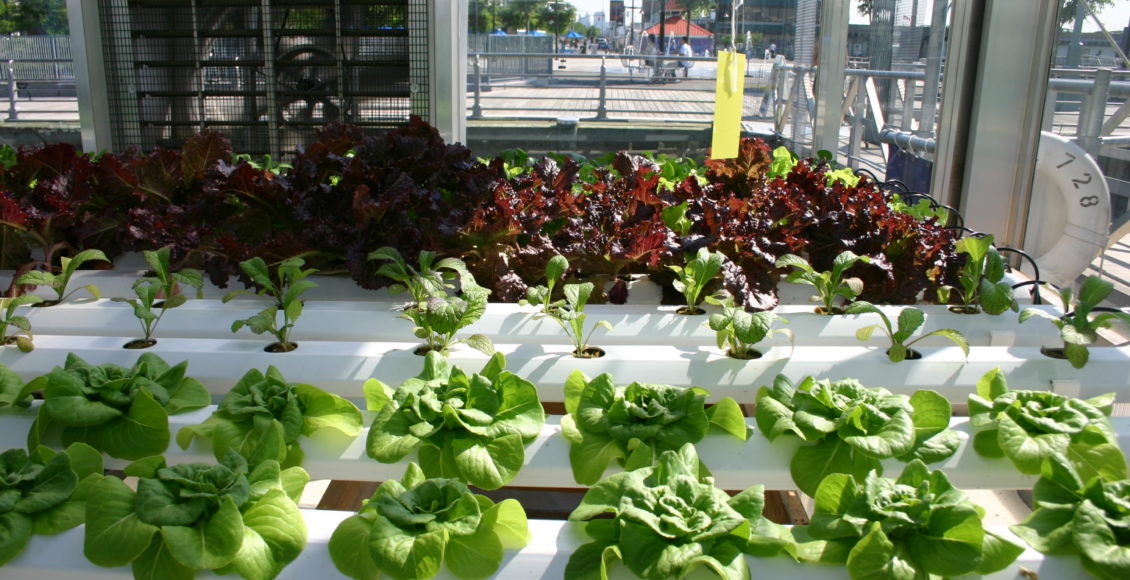
Hydroponics is the cultivation of plants by placing the roots in liquid nutrient solutions rather than in soil (soilless growth of plants and without conventional soil). It uses artificial means to support and nutrient solutions to provide the required nutrition to plants. (Picture shows salad greens grown by hydroponics.)ii Based on the way the solution is delivered, there are number of sub-types within the broad term of hydroponics iii . A synthesis of the pros and cons of hydroponics is summarized in the adjacent illustration Figure 1. iv
This technology becomes increasingly relevant given the food security issues raised by FAO. FAO estimates 60% increase in food production by 2050 compared to 2005. The three major resources for agriculture – land, water and labor are under increasing pressure from growing population and climate change. Only 5% of existing land can be expanded; mainly in Africa and Latin America. While 2 liters of water are often sufficient for daily drinking purposes, it takes about 3,000 liters to produce the daily food needs of a person. Urban population has already overtaken rural population and is expected to be twice that of rural population by 2050. The growth in cereal crop yields are slowing. There are other problems and uncertainties like climate change, natural disasters, bio-fueland post-harvest losses v .
While the hydroponics technology has been in existence for more than 50 years, the adoption and acceptance has been very low till date probably due to the high capital investment required, running costs and expertise neede vi . It forms a miniscule percentage (<0.1%) of overall global cultivation vii . There is mixed opinion on the question of hydroponics vs. conventional grown food among farmers and chefs viii in terms of taste and consumer acceptance. With forthcoming nutritional research, this aspect is only going to get better.
Hydroponics is poised to become increasingly relevant due to its inherent advantages to combat land, water, labor shortages while being environment and technology friendly. Future of this technology can be assessedby benefits accruing to the early adopters e.g. Tokyo is growing hydroponic rice in a controlled environment achieving four crop cycles instead of one; Organitech, a company in Israel, has overcome dry and arid climate, and is growing crops like bananas, berries, citrus fruits and achieving yield many times more than conventional cultivation. ix
Aeroponics for seed potato production has been found to be very advantageous (see picture) x.
It is known to produce higher potato yields (up to 10-times higher), in shorter duration and at lesser cost than conventional growing methods. It is already successfully used in many parts of the world – e.g. Korea, China and Central Andean regions – for more than 10 years. Performance of seed produced through aeroponics is same as the conventional seeds.
Based on the success of the technology in commercial production of many crops and seed production of potato, academia and seed industry may further explore the potential of this technology in seed production of other crops. Going forward xi , many technologies such as LED lighting (with ability to offer tailored spectrums to influence plant growth) and solar powered pumps will be integrated into hydroponics making it more accessible to industry and farmers.
In India, the central and state government have subsidized the capital costs for farmers willing to invest in hydroponics. Exact subsidy applicable is different for each state. Recently Maharashtra government xii has provided 50% subsidy to farmers to adopt hydroponics for growing animal fodder.
Author
i http://seedmeetstechnology.com/en/accessed on 25 Jan 2017
ii Picture attribute: By Ryan Somma – Leafy Greenhouse, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=7928074 accessed on 25 Jan 2017
iii http://www.johnnyseeds.com/growers-library/vegetables/hydroponics-trialing-about-johnnys.html accessed on 25 Jan 2017
iv http://www.slideshare.net/vishy62/hydroponicsan-explosive-fact-of-our-times accessed on 25 Jan 2017
v http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/rap/files/speech/131010-ava-ppp.pdf accessed on 25 Jan 2017
vi http://www.slideshare.net/vishy62/commercial-hydroponics-is-it-viable accessed on 25 Jan 2017
vii https://rirdc.infoservices.com.au accessed on 25 Jan 2017
viii Sardare, M.M.D. and Admane, M.S.V., 2013. A review on plant without soil-hydroponics. Int J Res EngTechnol, 2, pp.299-305
ix http://cipotato.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/005447.pdf accessed on 25 Jan 2017
x https://www.maximumyield.com/new-trends-in-hydroponic-growing-what-to-expect-in-2016-and-beyond/2/1423 accessed on 25 Jan 2017
xi http://indianexpress.com/article/cities/pune/fodder-shortage-farmers-to-adopt-hydroponic-method/ accessed on 25 Jan 2017
 Grow Beyond
Grow Beyond