Enhancing Traceability in Seed Value Chain by Digitization
The seed carries a potent value in the agriculture sector. Farmers having access to high-quality seeds are likely to achieve desirable crop production volume and earn more income. Seed traits such as germination percentage, purity, physiological vigour, moisture content, etc., are certain important preliminary parameters for determining healthy crops. Tracing the pedigree of seeds planted will help reduce overall farm and consumer level risk and provide accurate information that can further assist in precisely defining safety and quality control issues in the seed sector.
Certain evident traceability challenges exist in the seed industry such as inadequate information related to protocols being followed during seed production and processing process, inability to identify if there is any malicious mixing of quality seed with sub-standardized quality seeds. Several scams have surfaced where the state agricultural departments have received complaints from farmers on the failure of seed germination or seed condition deteriorating even before cultivation. Apart from this, there is still a paper-based system to keep records that makes it much more challenging to exchange information within the seed industry.
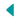
Digitization is one such solution that holds immense potential in developing traceability in the seed industry. It broadly involves capturing, structuring, and transmitting adequate information concerning the origin of the seed, parental lines of crops, phytosanitary treatments and protocols followed across the production process, and various handling steps involved in seed processing and marketing across the supply chain as indicated in figure 1.
There have been some notable movements in the seed digitization space. Recently, Agriculture Minister launched a national seed traceability mobile app for farmers, Telangana was declared as the first Indian state to implement seed traceability system across the state. It is a simple software system, where with the help of QR codes, a farmer will be able to trace quality and purity of seeds. The QR code will provide critical information such as time and manufacturer details, processing and packaging locations, seed quality test results and expiry details. There are some active start-up players such as Cropln, providing break-through traceability solutions across seed value chain.
Digital Interventions will not only help in achieving symmetrical information flow across the seed value chain but also will help critical value chain stakeholders to leverage on data and derive demand-driven strategies. It will also strengthen seed exports to developed countries by ensuring conformity with seed quality and improved efficiency. Furthermore, such network of digital systems will bring transparency, ensuring a significant reduction in malpractices and seed quality adulteration, which is one of the most prevalent issues existing in the seed industry.
Author

Connect with Author at: E-mail agribusiness@sathguru.com
 Grow Beyond
Grow Beyond