From Farm to Aisle: The Evolution of Fresh Fruits and Vegetables in Retail in India
Introduction
India, renowned for its rich biodiversity and agriculture, stands as a global powerhouse in the cultivation of fruits and vegetables. The dynamic landscape of the fruits and vegetable industry is influenced by elements of production, consumption, and the transformative role of modern retail. As global markets continue to evolve, modern retailers have strategically positioned themselves as key orchestrators in this agricultural symphony, implementing innovative strategies to enhance the entire supply chain. This article explores production, consumption patterns, and the pivotal influence of modern retail. Delving into the strategic initiatives undertaken by retailers, we examine how they navigate the evolving demands of consumers, particularly the rising preference for clean, exotic, and safe produce. Join us as we dissect the complexities of this flourishing industry, providing insights into the present and future dynamics that shape the landscape of F&V.
Current State of Fruit and Vegetable Production in India
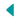
India is the second largest producer of F&V after China. Globally, ~100 Million Metric Tonnes of Fruits and ~1100 Million Metric Tonnes of Vegetables were produced in 2022. (FAO, 2022)
 In the fiscal year 2022-23, India recorded exports of fresh fruits and vegetables amounting to 1635.95 USD million. This included fresh fruits valued at 770.70 USD million and vegetables valued at 865.24 USD million. (APEDA)
In the fiscal year 2022-23, India recorded exports of fresh fruits and vegetables amounting to 1635.95 USD million. This included fresh fruits valued at 770.70 USD million and vegetables valued at 865.24 USD million. (APEDA)
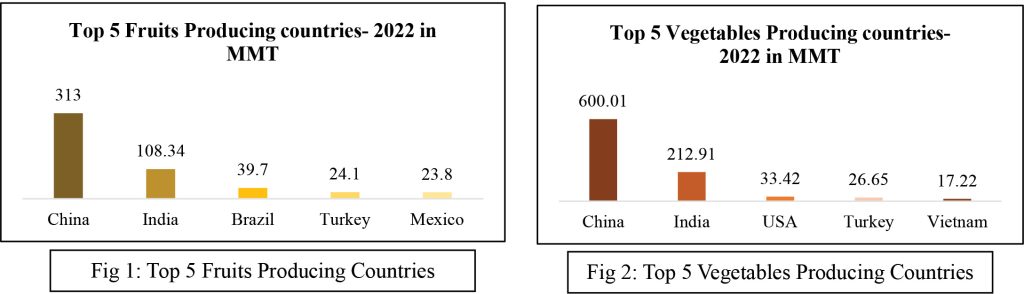
In India, a total of 104.34 and 212.91 million Metric tonnes of F&V were produced in 2022, respectively. The total output value of F&V in 2022, was estimated to be INR 3.75 Trillion. Andhra Pradesh is the largest fruit-producing state with 19 MMT contribution, and Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of Vegetables with 28.5 MMT contribution. (NHB, 2022)
 One major change in production patterns is the adoption of greenhouse and hydroponic farming methods. These techniques enable farmers to grow F&V in controlled environments, regardless of seasonality or geographical limitations. This has led to a substantial increase in production, as well as the ability to grow more exotic and out-of-season varieties. Additionally, advances in agricultural technology, such as the use of precision farming and automation, have further improved production efficiency and reduced the reliance on manual labour.
One major change in production patterns is the adoption of greenhouse and hydroponic farming methods. These techniques enable farmers to grow F&V in controlled environments, regardless of seasonality or geographical limitations. This has led to a substantial increase in production, as well as the ability to grow more exotic and out-of-season varieties. Additionally, advances in agricultural technology, such as the use of precision farming and automation, have further improved production efficiency and reduced the reliance on manual labour.
Consumption Patterns and Trends
- Traditional Consumption Habits: In India, consumption is shaped by seasonal availability, regional diversity, and cultural events. Dietary choices align with specific fruits and vegetables celebrated in peak seasons, while culinary practices integrate local produce. Religious and cultural events influence symbolic food choices. Street food culture creatively features fruits and vegetables in popular snacks.
- Shifting Dietary Patterns and Urbanization: Modern retail has revolutionized the way F&V is purchased and consumed. Supermarkets and grocery stores now offer a wide variety of F&V options, often sourced from multiple suppliers and regions. This has increased the availability of F&V to consumers, allowing them to access fresh produce conveniently. Moreover, the introduction of pre-cut and pre-packaged F&V has made it even easier for consumers to incorporate these nutritious items into their diets. Concurrently, a health and wellness wave is fostering an appreciation for fresh and safe produce. Culinary fusion, on-the-go snacking trends, and environmental consciousness among urban consumers further characterize this shift.
- The pandemic caused a notable shift in consumption habits, with consumers switching from unpackaged to packaged options for processed F&V due to hygiene concerns. Processed products, known for their long expiration dates, became ideal for home stockpiling during uncertain times.
- There is also a notable rise in the consumption of exotic varieties of F&V in India. Among fruits, Berries, Avocados, Rambutan, Mangosteen, Persimmons, Passion fruit, Kiwi and Dragon fruit are the most consumed varieties. Among vegetables, Olives, Lettuce, Broccoli, Jalapenos, Asparagus, Zucchini, Brussels sprouts, Celery, and Bell Peppers are the most sought-after.
Emergence of Modern Retail as an Organized Supply Channel
The fruits and vegetables sector in India is experiencing a notable transformation with the rising influence of modern retail formats, particularly supermarkets and hypermarkets. ~40% rise has been recorded in the sales of F&V in 2022, reflecting a growing reliance on organized supply channels. Consumers are increasingly drawn to these outlets due to the convenience they offer, providing one-stop shopping for a diverse array of fresh produce. This shift is marked by improved supply chain efficiency, technology integration, and regional penetration into tier II and III cities. As a result, modern retail not only ensures better stock control but also instils trust in consumers regarding the quality and safety of fruits and vegetables, thereby reshaping consumer behaviour and market dynamics.
- Rise of Supermarkets and Hypermarkets: As per a MOFPI study, there are a total of 44,842 hypermarkets in India as of September 2023. In today’s modern world, the retail industry plays a significant role in the production and consumption of fresh fruit and vegetables (F&V). The rise of modern retail has revolutionized the way F&V are sold and purchased, making them more accessible than ever before. Supermarkets and grocery stores have become the go-to destinations for consumers looking to purchase F&V. These retailers offer a wide variety of options, sourced from multiple suppliers and regions. The convenience and availability of F&V in these stores have made it easier for consumers to incorporate fresh produce into their diets.
Strategies Implemented by Modern Retailers
Modern retail has also brought about changes in the way F&V is marketed and displayed. Retailers have implemented strategies to enhance the visual appeal of F&V, using attractive displays, signage, and lighting to entice customers. Additionally, advancements in packaging and labelling have improved the quality and safety of F&V, providing consumers with the confidence to make their purchases.
- Store Layout Optimization:
- Fresh Produce Aisles: Modern retailers recognize the importance of creating visually appealing and accessible fresh produce sections within their stores. Well-designed aisles dedicated to fruits and vegetables enhance customer experience, making it easier for shoppers to navigate and explore a wide variety of options.
- Strategic Placement: Placing high-demand and seasonal produce strategically throughout the store encourages impromptu purchases. End-of-aisle setups, promotional areas, and attractive signage draw attention to fresh offerings, stimulating consumer interest.
- Innovative Sourcing Models:
- Farm-to-Fork Model: Retailers often work directly with farmers and suppliers to ensure a steady supply of fresh produce. Establishing direct relationships with local farmers and growers enables retailers to streamline the supply chain, reduce intermediary costs, and ensure a consistent flow of fresh produce. This approach not only supports local agriculture but also enhances the authenticity and traceability of the products.
- Aggregator Platforms: Some retailers leverage technology-driven aggregator platforms to connect with multiple suppliers, fostering a diverse and reliable sourcing network. This approach helps in maintaining a continuous supply of fruits and vegetables while ensuring competitive pricing.
- Quality Maintenance Protocols:
- Cold Chain Infrastructure: Investing in robust cold chain infrastructure is critical for preserving the freshness and nutritional value of fruits and vegetables. Modern retailers often deploy advanced refrigeration systems, transportation, and storage facilities to maintain an unbroken cold chain from farm to shelf.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Implementing dedicated quality assurance teams helps in monitoring and maintaining the desired quality standards. These teams work closely with suppliers to ensure adherence to quality benchmarks, including appearance, taste, and nutritional content.
- Traceability Systems: Employing traceability systems such as barcoding or QR codes facilitates real-time tracking of the supply chain. This not only enhances transparency but also allows for prompt identification and removal of products that may not meet quality standards.
The rise of modern retail sales has undoubtedly transformed the F&V market, making fresh produce more accessible, attractive, and convenient for consumers. With retailers continuously innovating and adapting to consumer demands, the growth of F&V in modern retail shows no signs of slowing down.
Conclusion and Way Forward
Within India’s fruits and vegetables sector, the dynamic interplay of production, consumption, and the strategic impact of modern retail showcases the nation’s agricultural excellence. The changing consumption landscape, influenced by traditional habits and urbanization, highlights the sector’s adaptability. Modern retail, witnessing a substantial surge in sales, emerges as a pivotal force, reshaping procurement, distribution, and consumer behaviour. The industry’s trajectory reflects a harmonious blend of tradition and innovation, promising a compelling future. To sustain and augment this growth, stakeholders must prioritize continued integration of technology, ensuring efficient supply chain management and quality assurance. Collaborations with local farmers, adoption of sustainable swaps, and robust cold chain infrastructure are imperative for preserving the freshness and nutritional integrity of fruits and vegetables. A forward-looking approach should embrace sustainable practices, aligning with evolving consumer preferences for clean, exotic, and safe produce.
Author:

Associate Consultant – Food Processing and Retail practice
Connect with Author at: E-mail foodbiz@sathguru.com
 Grow Beyond
Grow Beyond